Balance Sheet Format, Explanation and Example
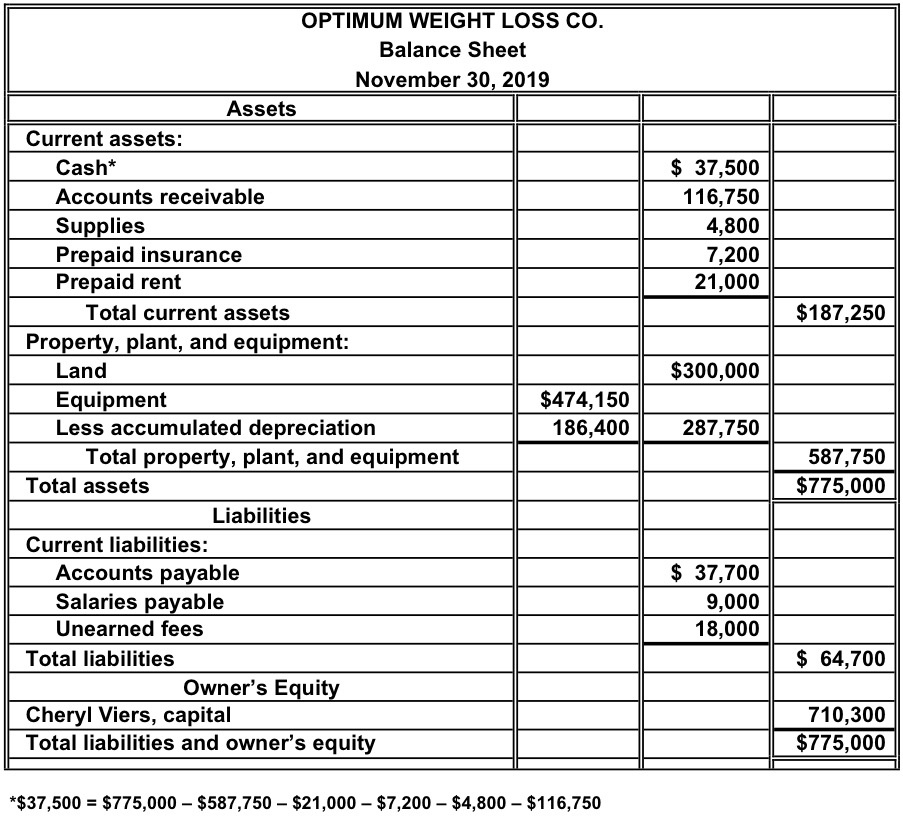
In both cases, the external party wants to assess the financial health of a company, the creditworthiness of the business, and whether the company will be able to repay its short-term debts. The balance sheet previews the total assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity of a company on a specific date, referred to as the reporting date. A balance sheet is a financial statement that shows the relationship between assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity of a company at a specific point in time. Current assets refer to assets that a company can easily convert into cash within a financial year. This category includes readily available funds in the bank, inventory stock, and accounts receivable, which is money owed to the company by its customers.
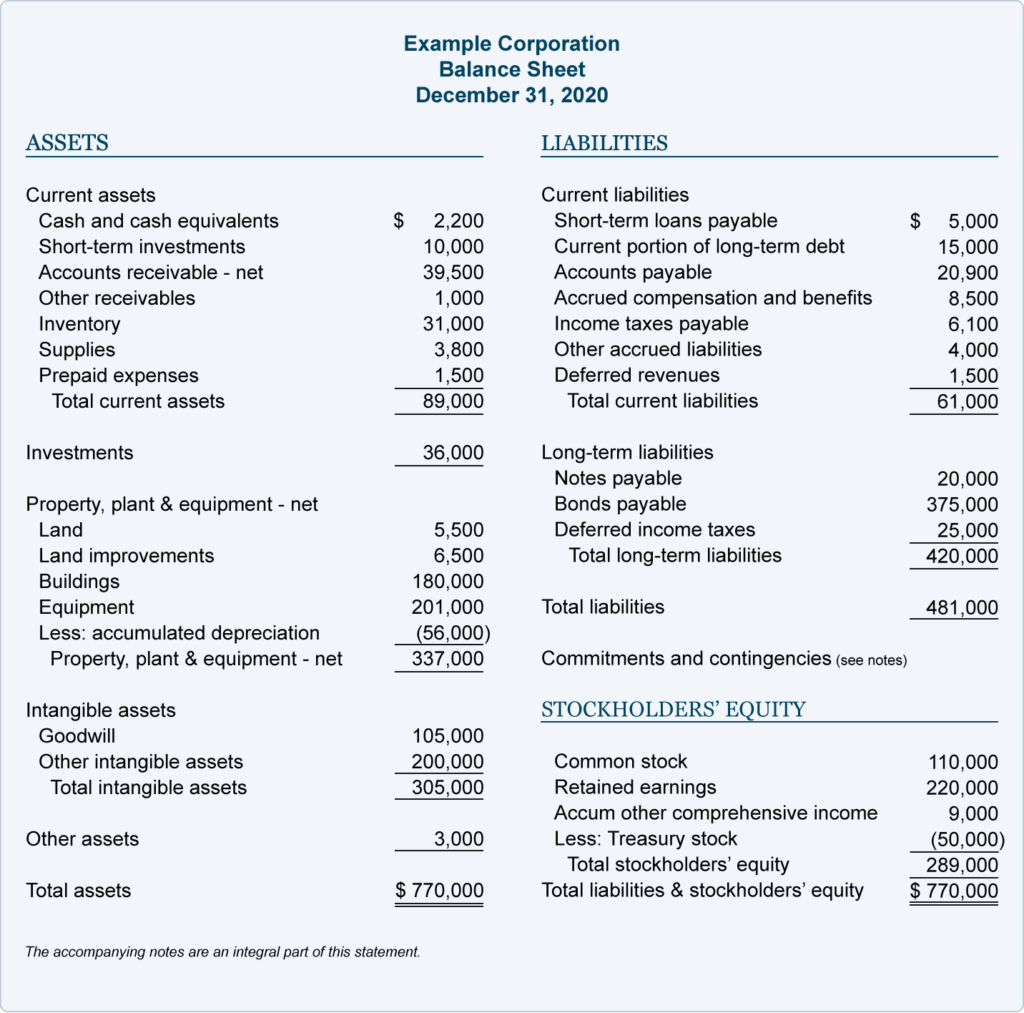
What is included in the balance sheet?
With a firm understanding of the balance sheet basics, you can use this report to guide financial decision-making in your business. Although it takes time and effort to create an accurate balance sheet from scratch, it is a vital report you as a business owner should have. Looking for an even simpler way to create balance sheets that support your business? FreshBooks’ free balance sheet template will help you keep track of all the information you need to manage your numbers with ease, helping you to check balances and keep your finances in order.
Who prepares balance sheets?
The balance sheet only reports the financial position of a company at a specific point in time. Assets are typically listed as individual line items and then as total assets in a balance sheet. This may include accounts payables, rent and utility payments, current debts or notes payables, current portion of long-term debt, and other accrued expenses. Another difference is that the accounting balance sheet gives more detail, whereas the operating balance sheet does not. For example, the balance sheet shows only “tangible fixed assets”, without going into detail. These two balance sheets are distinct, but the operating balance sheet is based on data from the accounting balance sheet.
Ask Any Financial Question
Current Liabilities – A current liability is a loan due to creditors within the next 12 months from the beginning date of the reporting period. Non-current assets here include both tangible and intangible assets of an entity. A higher debt-to-equity ratio means the company relies more on debt to finance its operations. This could signify financial trouble if the debt is not being paid back. The balance sheet is organised into distinct sections, each displaying the total of corresponding accounts along with their respective sub-accounts and balances.
The balance of equity is affected by an income statement as well as assets and liabilities. Current liabilities include short-term loans, accounts payable, and others payable that the company will need to pay within twelve months. The assets are made up of fixed and intangible assets, bank, stock and debtors.
- Finally, since Bill is incorporated, he has issued shares of his business to his brother Garth.
- Our team is ready to learn about your business and guide you to the right solution.
- Noncurrent assets are long-term investments that the company does not expect to convert into cash within a year or have a lifespan of more than one year.
- FreshBooks’ free balance sheet template will help you keep track of all the information you need to manage your numbers with ease, helping you to check balances and keep your finances in order.
- It should not be surprising that the diversity of activities included among publicly-traded companies is reflected in balance sheet account presentations.
- External auditors, on the other hand, might use a balance sheet to ensure a company is complying with any reporting laws it’s subject to.
On the other side, you’ll put the company’s liabilities and shareholder equity. According to the historical cost principle, all assets, with the exception of some intangible assets, are reported on the balance sheet at their purchase price. In other words, they are listed on the report for the same amount of money the company paid for them. This typically creates a discrepancy between what is listed on the report and the true fair market value of the resources. For instance, a building that was purchased in 1975 for $20,000 could be worth $1,000,000 today, but it will only be listed for $20,000.
Investors and lenders also use it to assess creditworthiness and the availability of assets for collateral. A balance sheet is also different from an income statement in several ways, most notably the time frame it covers and the items included. Using financial ratios in analyzing a balance sheet, like the debt-to-equity ratio, can produce a good sense of the financial condition of the company and its operational efficiency. Adding total liabilities to shareholders’ equity should give you the same sum as your assets.
Noncurrent assets are long-term investments that the company does not expect to convert into cash within a year or have a lifespan of more than one year. However, it is crucial to remember that balance sheets communicate information as of a specific date. It is also possible to grasp the information found in a balance sheet to calculate important company metrics, such as profitability, liquidity, and debt-to-equity ratio.
Balance sheets are important financial statements that provide insights into the assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity of a company. The report provides helpful information when assessing a company’s financial stability. Financial ratios are used to calculate the business’s financial position, including liquidity and gearing ratios. Banks and suppliers use them to determine if they can offer a loan, overdraft or credit facility. This includes debts and other financial obligations that arise as an outcome of business transactions.
Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of cost centres define where costs are incurred our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. For instance, accounts receivable should be continually assessed for impairment and adjusted to reveal potential uncollectible accounts.

