How to Read & Understand a Balance Sheet
The higher the ratio, the better your financial health in terms of liquidity. A company can use its balance sheet to craft internal decisions, though the information presented is usually not as helpful as an income statement. A company may look at its balance sheet to measure risk, make sure it has enough cash on hand, and evaluate how it wants to raise more capital (through debt or equity). In this example, Apple’s total assets of $323.8 billion is segregated towards the top of the report.
Liquidity
Explore our eight-week online course Financial Accounting—one of our online finance and accounting courses—to learn the key financial concepts you need to understand business performance and potential. Below liabilities on the balance sheet is equity, or the amount owed to the owners of the company. Since they own the company, this amount is intuitively based on the accounting equation—whatever assets are left over after the liabilities have been accounted for must be owned by the owners, by equity. These are listed at the bottom of the balance sheet because the owners are paid back after all liabilities have been paid. Also called the acid test ratio, the quick ratio describes how capable your business is of paying off all its short-term liabilities with cash and near-cash assets.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
- Excel is an excellent tool to design your own if you are not using accounting software.
- It is one of the three core financial statements (income statement and cash flow statement being the other two) used for evaluating the performance of a business.
- Some executives may fiddle with balance sheets to make businesses look more profitable than they actually are.
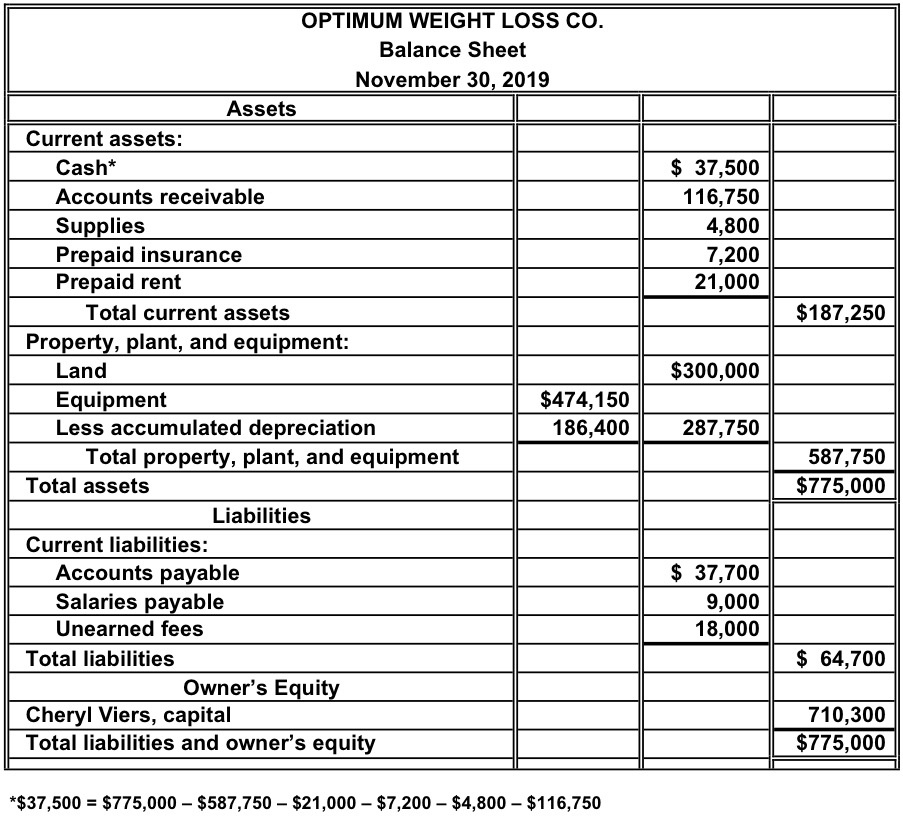
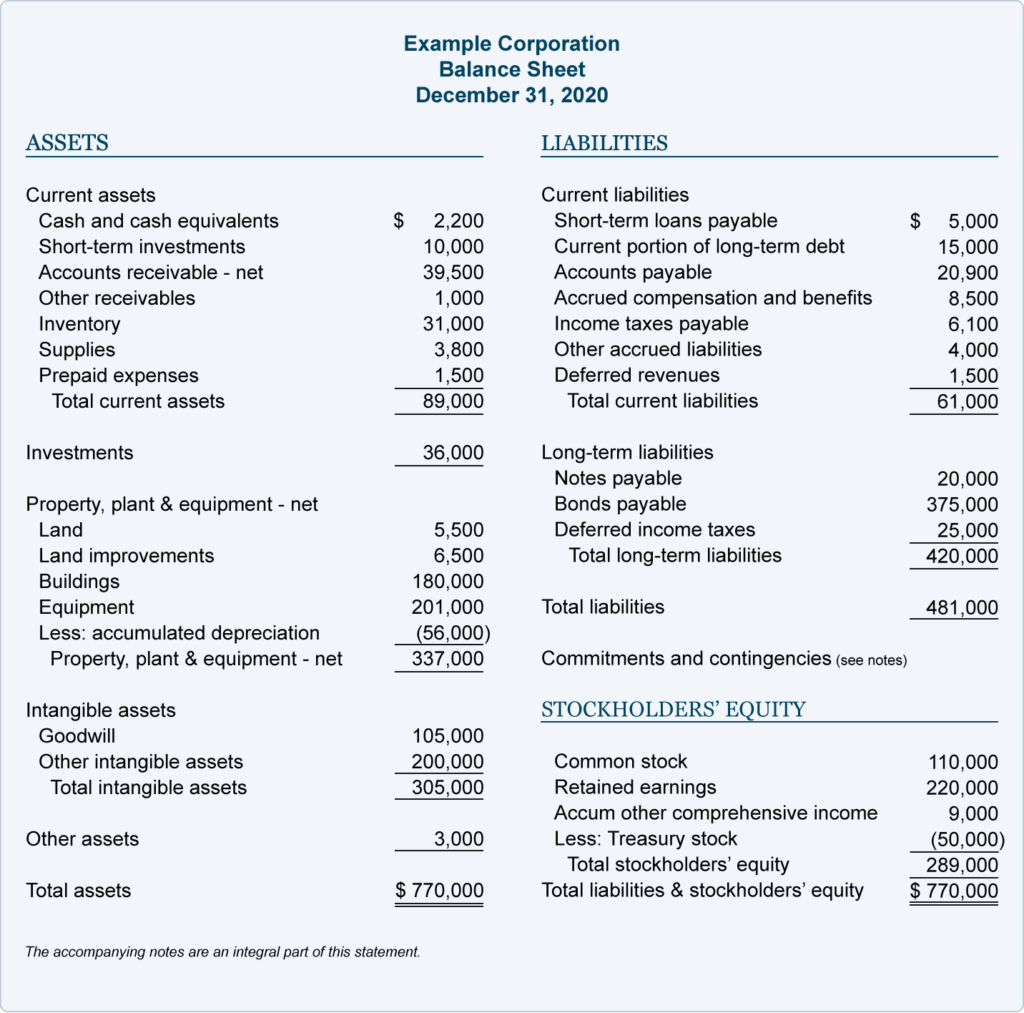
- A balance sheet is meant to depict the total assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity of a company on a specific date, typically referred to as the reporting date.
- Explore our finance and accounting courses to find out how you can develop an intuitive knowledge of financial principles and statements to unlock critical insights into performance and potential.
Balance sheets of small privately-held businesses might be prepared by the owner of the company or its bookkeeper. On the other hand, balance sheets for mid-size private firms might be prepared internally and then reviewed over by an external accountant. The data and information included in a balance sheet can sometimes be manipulated by management in order to present a more favorable financial position for the company.
FAQs About Balance Sheets
Balance sheets are important because they give a picture of your company’s financial standing. Before getting a business loan or meeting with potential investors, a company has to provide an up-to-date balance sheet. A potential investor or loan provider wants to see that the company is able to keep payments on time. Because it summarizes a business’s finances, the balance sheet is also sometimes called the statement of financial position. Companies usually prepare one at the end of a reporting period, such as a month, quarter, or year.
In the example below, we see that the balance sheet shows assets (such as cash and accounts receivable), liabilities (such as accounts payable, credit cards, and taxes payable), and equity. Total liabilities and equity are also added up at the bottom of the sheet—hence the term ‘bottom line’ for this number. A balance sheet is one of the most essential tools in your arsenal of financial reports. Generally speaking, balance sheets are instrumental in determining the overall financial position of the business.
Shareholder Equity
By analysing balance sheet, company owners can keep their business on a good financial footing. Liabilities are obligations to parties other than owners of the business. They are grouped as current liabilities and long-term liabilities in the balance sheet. Current liabilities are the obligations that are expected to be met within a period of one year by using current assets of the business or by the provision of goods or services. All liabilities that are not current liabilities are considered long-term liabilities. The fundamental accounting equation states that a company’s assets must be equal to the sum of its liabilities and shareholders’ equity.
The balance sheet provides an overview of the state of a company’s finances at a moment in time. It cannot give a sense of the trends playing out over a longer period on its own. For this reason, the balance sheet should be compared with those of previous periods. Although balance sheets are important, they do have their limitations, and business owners must be aware of them. It is also helpful to pay attention to the footnotes in the balance sheets to check what accounting systems are being used and to look out for red flags.
What is the purpose of a contribution in the form of a shareholder’s current account? Find out how this alternative form of financing works, and what its many advantages are. If the WCR is positive, this means that the company has little or no trade payables, but does have stock and trade receivables. In this case, it may be a good idea to review customer follow-up and sales management. For example, if the corporation is the bank, then the central banks might require the corporation to have certain amounts of capital reserve for liquidation. Common Stock or Ordinary shares are the same, and this class of shares normally has voting right.
Companies might choose to use a form of balance sheet known as the common size, which shows percentages along with the numerical values. As noted above, you can find payroll bookkeeping information about assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity on a company’s balance sheet. The assets should always equal the liabilities and shareholder equity.
Not sure where to start or which accounting service fits your needs? Our team is ready to learn about your business and guide you to the right solution. It can be sold at a later date to raise cash or reserved to repel a hostile takeover. We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources.
The balance sheet equation follows the accounting equation, where assets are on one side, liabilities and shareholder’s equity are on the other side, and both sides balance out. All assets that are not listed as current assets are grouped as non-current assets. A common characteristic of such assets is that they continue providing benefit for a long period of time – usually more than one year. Examples of such assets include long-term investments, equipment, plant and machinery, land and buildings, and intangible assets. In the asset sections mentioned above, the accounts are listed in the descending order of their liquidity (how quickly and easily they can be converted to cash).


